In July 2023 we focused on sulphur silanes. This month our focus will be on vinyl silanes. We did cover the introductory part in that article. However, at the risk of being repetitious, but for a stand-alone reader, we will repeat it here…
Introduction
Silanes have been known for about 50 years. They were originally used in an industrial scale for adhesives and coatings. In the 70s silanes found their way into the rubber industry as coupling agents for white filler. During the early 90s, sulphur silanes gained more importance due to the increasing acceptance of the Green Tyre. The use of silane coupling agents as surface treatments, adhesion promoters or cross -linking agents has been growing significantly over the past decades. When used in sealants, adhesives, coatings, rubbers or even surface primers, silane can provide major improvements in adhesion on various substrates.
When used as cross-linkers by development technologist, compounders and moulders, silanes will improve abrasion resistance stiffness and heat resistance as well as dynamic properties of the finished products.
Organofunctional silanes will hydrolyze in the presence of moisture and condense onto the surface of different substrates and fillers, forming chemically covalent bonds between organics and inorganic substrates.
Silane categories
Depending upon the chemical composition, the main categories of silanes available are: sulphur, vinyl, epoxy, isocyanate, amino, chloro, methacryl and thiocyanate. In the rubber industry, sulphur and vinyl silanes are commonly used, whereas amino, chloro and others are rarely used.
The General Formula for silane
Although the chemical theory is sufficiently researched, the selection of the most suitable silane for specific elastomers and their vulcanization systems requires much know how. With silanes, not only a physical process takes place inside the mixing chamber, but also at the same time a chemical reaction called silanization takes place. Here the mixing parameters play an important role. Certain compound ingredients may promote the silanization or disturb this process, affecting the physical properties of the compound.

Silane products for the Rubber Industry
Deolink TESPT [bis(triethoxysilylpropyl)tetrasulfane] is a preparation with 50% active substance on a polymer/wax carrier system. It can be used in almost all elastomers which are suitable for sulphur vulcanization,
Deolink MX is a preparation of a thiocarboysilane with 50% active substance.
In comparison to the tetrasulfane silanes, Deolink MX can be processed over a broad temperature range without the risk of scorch. It can often be used even at lower dosages without loss of effectiveness. It has a blocked mercapto group and can be chosen as an alternative to conventional mercapto silanes. The protective group is removed during processing releasing the mercapto silane. By using Deolink MX, optimized processing properties can be achieved and the unpleasant odour of mercaptanes is avoided. Deolink MX is suitable for all elastomers which can be cross linked by sulphur vulcanization.
Observing how silanes react
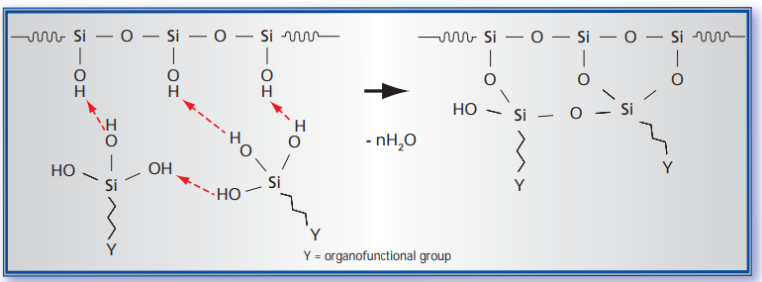
Generally, there are two theories. The first one describes a direct condensation, whilst the second is based on the pre-hydrolysis of the silane. Studies, however, are in favour of a two-step reaction with the following pre-reaction:
Pre-reaction
Hydrolysis (example: alkoxysilane)
The alcoxy groups of the silicium are subject to hydrolysis. The necessary water is usually available on the surface of the inorganic filler.

Step 1
Connection with the mineral surface (example: silica)
The silanol groups which are formed by the hydrolysis of the silane, condense with the hydroxyl groups of the filler and form stable Si-O-Si bonds by splitting off water.
Step 2
Linking with the polymer matrix (example: mercapto silane)
The organofunctional group (Y) is relevant for the reaction with the polymer. This reactive group must be suitable for the chosen vulcanization system, to enable cross linking during the vulcanization process.
Using this mechanism, it is possible to form a silane bridge through a chemical reaction between the polymer chains and the filler particles. This process results in the formation of a polymer filler network.
Reaction of a silanized filler with the polymer (example: mercapto silane)
Applications for technical rubber compounds
Cables/cable accessories: Improved electrical properties (insulation, water absorption, swelling, dielectrical strength), improved mechanical properties (tensile strength, abrasion).
Roller coverings: Reduced abrasion, improved compression set, improved dynamic properties (heat buildup), optimized processing properties.
Sealings/O-rings: Improved compression set, optimized processing properties, improved mechanical properties, reduced abrasion, for dynamically stressed sealings.
V-Belts/conveyor belts: Reduced abrasion, improved dynamic properties, improved adhesion with the reinforcing fabric
Shoe soles: Reduced abrasion, optimized processing properties, improved dynamic properties (flex cracking resistance)
Moulded articles: Improved dynamic properties, optimized processing properties, improved mechanical properties.
Hoses & tubes: Reduced abrasion, improved mechanical properties, improved adhesion with the reinforcing fabric.
It is quite evident that these DOG carrier systems of silanes have significant advantages in improved protection against hydrolysis through moisture, excellent dispersion and handling, easy incorporation without spots, no formation of agglomerates, no dust development by fines, prolonged storage stability without loss of activity and cost savings to complete use of opened boxes, no disposal of ineffective hydrolized residues. Other added advantages are shelf life, reactivity retention and less storage sensitive.
Product Description
Vinyl silanes – Deolink Vinyl/Deolink VO/Vinyl VE
Deolink VO (oligomeric siloxane containing vinyl, propl and ethoxy groups) and Deolink Vinyl {Tris (2-methoxyethoxy) vinylsilane} are used to improve the physical properties of peroxide cured compound and to establish chemicals links between organic polymers and inorganic fillers (e.g. silica, clay, aluminum trihydrate). With Deolink VO/Deolink Vinyl, the processing and the wet electrical properties can be improved, which is of importance for the cable industry
Deolink Vinyl forms toxic Methoxyethanol during vulcanisation and therefore it might be registered as a substance of very high concern in the future.
Based on oligomeric siloxane, Deolink VO does not form Methoxyethanol and in comparison, to conventional vinyl silanes the amount of ethanol released is significantly reduced – this leads to lower VOC (volatile organic compounds). Deolink VO provides similar or even better mechanical properties as well as improved long-term electrical properties.
Deolink VE is a polymeric silane preparation containing 50% of an oligomeric siloxane having vinyl and ethoxy groups. Deolink VE establishes a chemical link between organic polymers and inorganic fillers (e.g., silica, clay aluminum trihydrate) and improves physical properties such as compression set or abrasion resistance of peroxide cured compounds.
Through the use of Deolink VE, processing and wet electrical properties can be improved, which is of importance for the cable industry. Based on an oligomeric siloxane, Deolink VE does not form any toxic Methoxyethanol (EGME). A further advantage of Deolink VE is a lower VOC, since the amount of ethanol that is released during hydrolysis is significantly reduced.
Properties
DOG offers three vinyl silane preparations, which differ in the active substance and in the carrier systems.
-
- Deolink Vinyl: Tris(2-methoxyethoxy) vinyl-silane on an EVA/paraffin wax carrier system and is well established in the rubber industry. It is a traditional vinyl-functional coupling agent, that improves mechanical and we-electrical properties of radically cross-linked elastomers. During hydrolysis Deolink Vinyl generates 2 – Methoxyethanol, which is identified as SVHC substance according to Regulation (EC) 1907/2006 REACH
- Deolink VO: Polysiloxane on polymer/ wax carrier. Oligomeric vinyl-functional coupling agent combined with longchain alkoxy silane. Deolink VO is particularly suitable for cables. The specific combination of coupling and wetting agent improves wet-electrical and mechanical properties of radically cross-linked polymers. Deolink VO does not generate or liberate any 2-Methoxyethanol.
- Deolink VE: Polysiloxane on polymer/wax carrier. Oligomeric vinyl-functional coupling agent. Deolink VE provides excellent coupling efficiency for best mechanical properties of radically cross-linked polymers. Deolink VE does not generate or liberate any 2-Methoxyethanol and therefore is recommended as a replacement for traditional vinyl silanes.
Advantages
- Excellent dispersion and dosage
- Easy incorporation without spots
- Highly protected against humidity
- Improved physical properties
- Improved long term electrical properties
- For Deolink VO: No formation of Methoxyethanol by hydrolysis from the active substance.
Technical Information
Deolink VO/Deolink Vinyl/Deolink VE in an EPDM Cable Compound
| Batch 1111E | Control | Deolink VO | Deolink Vinyl | Deolink VE |
| Keltan 5470 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Clay | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Paraffinic Oil | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Controzon | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| TMQ | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 |
| Deolink Silane Preparation | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| TAC DL 70 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Perkadox 14-40 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| Total phr | 300 | 302 | 302 | 302 |
| MDF 2000 180 °C/6 min | ||||
| S’ min (dNm) | 1.28 | 12.24 | 1.25 | 1.41 |
| S’ max (dNm) | 22.34 | 22.26 | 22.65 | 23.85 |
| t10 (min) | 0.45 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.52 |
| t90 (min) | 3.11 | 3.39 | 3.31 | 2.85 |
| Mooney Viscosity | ||||
| ML 1+4, 100°C | 75 | 65 | 69 | 57 |
| Vulcanisation 10 min/180°C, S2-Specimen | ||||
| Modulus 100% (Mpa) | 4.3 | 8.5 | 8.3 | 8 |
| Tensile Strength (Mpa) | 15.3 | 14.7 | 15 | 16.4 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 546 | 292 | 276 | 227 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 71 | 73 | 74 | 73 |
| Heat Aging 72h/125 °C, S2 Specimen | ||||
| Tensile Strength (Mpa) | 12.7 | 17.2 | 16.6 | 18.8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 235 | 162 | 150 | 165 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 76 | 76 | 76 | 76 |
| Compression Set, Vulcanisation 15’/180°C | ||||
| 24h/100°C (%) | 29 | 11 | 13 | 9 |
| Immersion in H2O (dest) 168H/70°C | ||||
| Weight change (%) | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.3 |
| Rheovulkameter: Extrusion Test, 100 s preheating, nozzle/piston 90°C/35 har | ||||
| Volume after 70s (cm3) | 2.69 | 2.81 | 2.7 | 3.61 |
| Volume Resistivity according to DIN IEC 93 (test after storage in deionized water) | ||||
| Original (Ω) | 2.8 x 10¹² | 1.1x 10¹² | 1.2×10¹³ | 1.1 x 1013 |
| After 28 d/23°C (Ω) | 9.9 x 109 | 2.8 x 1011 | 6.9 x 1011 | 7.9 x 1012 |
Electrical Properties
In articles made for the electronics industry, the electrical properties are of particular importance. Silanes can provide a significant in put to improve the required performance. For unaged samples, the addition of silanes only show a small influence on the electrical properties. The major advantage of silanes can be observed, when measuring the electrical data after an ageing process. The control compound with unsilanized filler absorbs moisture and therefore reduces the insulation properties.
Compounds containing silanes show extreme improvements. The hydrophobation of the filler and the increased cross-linking density reduce the water absorption and keep the insulation properties constant.
Conclusion
Deolink VO and Deolink Vinyl are easy to incorporate and disperse in EPDM compounds and improves the processing and mechanical properties significantly. Especially the use of Deolink VO leads to a significantly lower Mooney viscosity and a remarkably improved compression set. The wet electric properties are also optimized with Deolink VO. Deolink VO does not form any toxic Methoxyethanol.
Deolink VO is an environmentally friendly and highly efficient oligomeric siloxane especially for the use in compounds targeted for electrical appliances.
Deolink VE improves mechanical as well as electrical properties. Deolink VE furthermore facilitates processing what is reflected in lower viscosity and better flow behaviour.
This completes our two-part article on silanes. Founded in 1902, D. O. G. are a family-owned company located in Hamburg’s free harbor. Being a specialist in additives with its own research and development facilities, D. O. G. have developed many liquid silanes and dry liquid blends for the rubber and coating industry. The development of user friendly and environmentally friendly products has been a tradition and long may it continue.
I R Tubes Pvt. Ltd. is a leading specialty chemical suppliers for the chemical industry. Contact I. R. Tubes on info@irtubes.com or Call: 9689927193 for more information